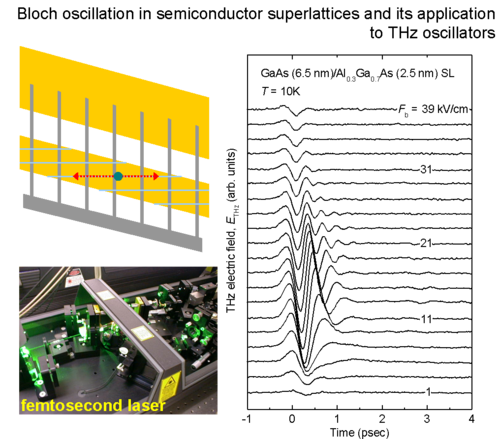
Semiconductor superlattice, proposed in 1970 by Esaki and Tsu, is a one-dimensional man-made periodic structure, which usually consists of a stack of two different semiconducting materials. It is known that a system with a periodic potential has a remarkable feature that electrons perform oscillatory motion when accelerated by dc electric fields (Bloch oscillation). Bloch oscillator is a device concept that utilizes such an oscillatory electron motion for realizing ultra-high frequency oscillators. We work on the dynamics of Bloch oscillating electron in semiconductor superlattices by using time-domain THz spectroscopy and explore possibilities of realizing THz Bloch oscillators.
We work also on large ac amplitude operation of superlattices to control the formation of high-field domains and design/analyze novel quantum cascade laser structures.
Topics
- Bloch oscillation and THz gain in semiconductor superlattices
- Suppression of high-field domains in semiconductor superlattices by large ac amplitude operation
- Analysis of carrier dynamics in THz quantum cascade lasers by using non-equilibrium Green’s function approach